
There are many symptoms of chlamydia infection, and some of them may seem harmless. While they are often ignored, a chlamydia infection can lead to serious complications, such as a blocked fallopian tube and pelvic inflammatory disease. In addition to symptoms, people with chlamydia should not engage in sexual intercourse until they have been treated with an antibiotic.
Most people with chlamydia infection have no symptoms. Some people may mistake the infection for other symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases or even a different disease. However, some people will develop painful vaginal discharge, painful urination, and a swollen penis. While these symptoms do not necessarily indicate you have chlamydia, they can be warning signs of a more serious infection.
There are several ways to notify your partner. You can visit your GP or sexual health centre to get the appropriate information. You can also opt for a confidential way to inform your partner. A confidential message will be sent to your partner, who should be notified within 7 days of becoming infected. Once your partner is notified, you should not have sex with him or her until you’re sure that you’re free from the symptoms.
Chlamydia infection symptoms do not manifest immediately. In most cases, symptoms may take weeks to appear, but in some cases, a person may experience them for weeks or even months. These symptoms can be confusing, and can be confused with those of other sexually transmitted diseases. Some other symptoms include painful urination, painful testicles, and vaginal discharge. The infection itself is often mild and unnoticeable, but the complications that can result are serious.
If you’re having sex with your partner, you’re at risk for contracting chlamydia. Infection can cause serious complications, and treatment is the best way to avoid chlamydia. While you may not be aware of it, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. If you have a new sexual partner, make sure you use barrier contraception to protect yourself.
Women should be screened for chlamydia every year. After treatment, you should repeat the test three months later. The same is true for women who engage in multiple sexual partners. While a woman who is pregnant should not undergo a test for chlamydia, it is still important to be screened for chlamydovirus infection. If a woman is pregnant, she should be screened at her first prenatal visit.
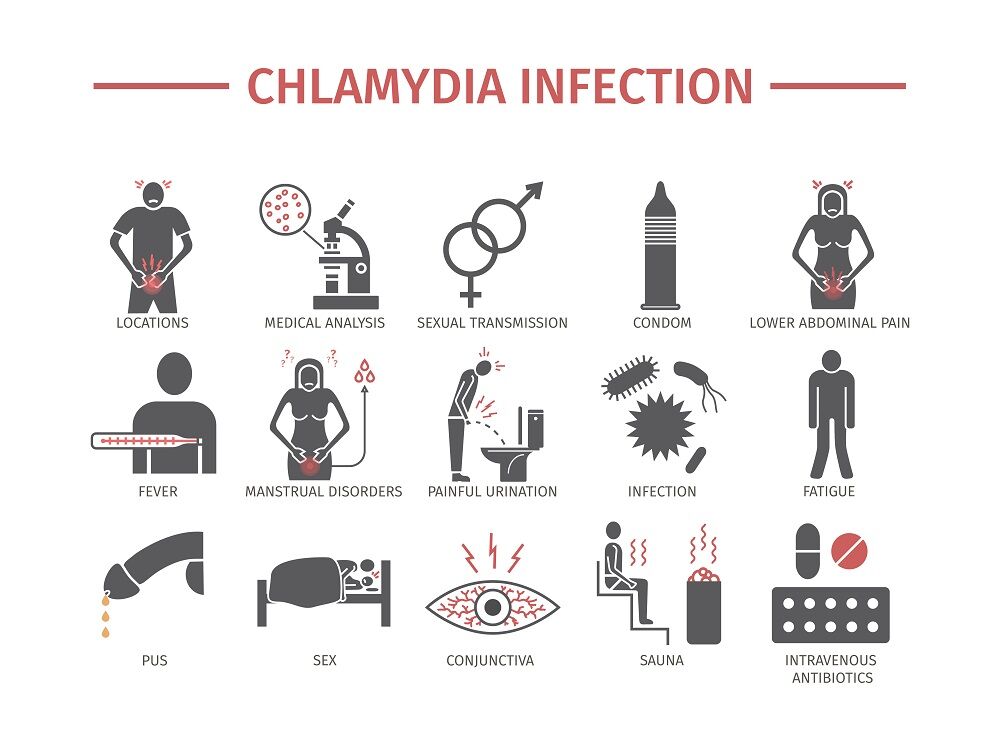
The symptoms of chlamydia are usually asymptomatic. However, untreated chlamydia can lead to more serious problems, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy. In women, chlamydia can also spread to the testicles and epididymitis. The infection may also lead to reactive arthritis and eye infections.
Chlamydia symptoms should be treated with antibiotics. If you have a confirmed case, you can have sex with your partner until your symptoms go away. If you suspect chlamydia, you should avoid sex until the symptoms are gone. The health website https://sagreinbasilicata.com/
will recommend appropriate medications based on your needs and your symptoms. You should also check all your partners. If you suspect infection of the sexual partner with chlamydia, it is necessary to undergo a second examination.
Untreated chlamydia can spread to the fallopian tubes and uterus, causing severe pelvic pain and infertility. The infection can even lead to an ectopic pregnancy, which can be fatal. It may also be passed to your baby during childbirth. If you are pregnant, you should be tested for chlamydia as soon as possible.
In most cases, chlamydia causes no symptoms and you can be treated with antibiotics to stop the infection. It can spread to other parts of the body and you should contact your healthcare provider if you experience any side effects. If you test negative, you must tell your partner that you have been diagnosed with chlamydia and are currently being treated for it. Otherwise, you risk re-infection and transmission to a partner.
Although chlamydia does not cause symptoms, it can be dangerous if left untreated. You should be tested for chlamydia as soon as possible after having sex with an infected person. You must have sexual relations with someone who has a history of chlamydia. At this time, you should also consider taking a sex test to check for an infection.